If you’ve ever wandered through a farmers’ market or grocery store, you’ve probably come across zucchini, a versatile summer squash used in countless recipes. But what about calabacita? The name might sound unfamiliar to some, but it’s a staple in many Latin American cuisines. This brings us to the big question: is calabacita the same as zucchini? While these two squash varieties share similarities, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this article, we’ll explore their origins, physical features, culinary uses, and more to give you a clear answer.
Table of Contents
What Is Calabacita?
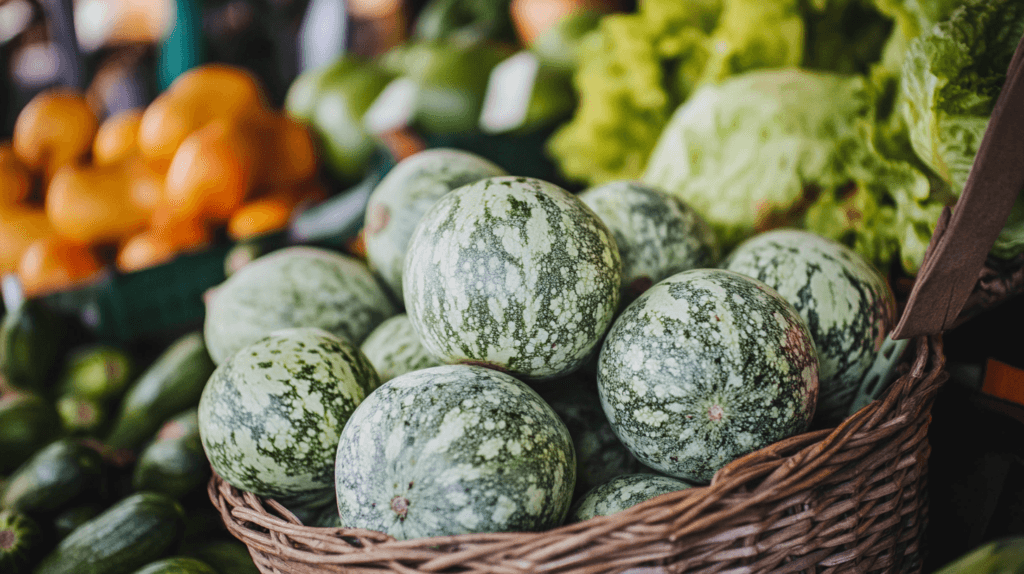

Etymology and Meaning of Calabacita
The term “calabacita” comes from Spanish, where “calabaza” means squash or pumpkin, and “calabacita” translates to “little squash.” In many Spanish-speaking regions, the word is used to describe various types of small squashes, especially those resembling zucchini in appearance and taste. Depending on the region, it might refer to a specific variety or be a general term for any small, tender squash.
Cultural and Regional Significance of Calabacita
Calabacita holds a special place in Latin American cuisines, particularly in Mexico and Central America. It’s a key ingredient in traditional dishes like calabacitas con elote (sautéed squash with corn) and sopa de calabacita (squash soup). Beyond its culinary use, calabacita is often grown in home gardens, symbolizing resourcefulness and a connection to the land.
Physical Characteristics of Calabacita
While calabacita can look similar to zucchini, it tends to be shorter and rounder, often with lighter green or speckled skin. Some varieties may even have a slightly bulbous shape. The flesh is tender and mild, making it ideal for quick-cooking methods like sautéing or grilling.
What Is Zucchini?
Origins and Historical Background of Zucchini
Zucchini, also known as courgette in Europe, is a summer squash that originated in the Americas but was cultivated and popularized in Italy during the 19th century. The zucchini we know today is a product of selective breeding, designed to produce a consistent, elongated shape and mild flavor.
Uses of Zucchini in Culinary Practices
Zucchini is celebrated for its versatility. It can be spiralized into noodles, stuffed and baked, shredded into fritters, or simply grilled with olive oil and herbs. Its mild flavor allows it to blend seamlessly into both savory and sweet recipes, such as zucchini bread.
Physical Features of Zucchini
Zucchini is typically elongated and cylindrical, with smooth, dark green skin. Some varieties may feature yellow or striped patterns, but the overall appearance is sleeker and more uniform than calabacita.
The Relationship Between Calabacita and Zucchini
Calabacita and zucchini are closely related members of the Cucurbitaceae family, which includes other squashes, pumpkins, and gourds. Both are classified as summer squash, meaning they are harvested when their skin is tender and their seeds are immature. Despite their similarities, they are distinct cultivars with unique characteristics.
Shared Origins
Both calabacita and zucchini originated from ancient varieties of squash cultivated in the Americas. Over time, selective breeding led to the development of zucchini in Italy during the 19th century, while calabacita remained popular in Latin American regions.
Regional Distinction
- Calabacita: Often found in Mexican and Central American markets, calabacita has deep cultural roots in traditional dishes.
- Zucchini: Widely popularized in Europe and the United States, zucchini is a staple in Mediterranean and Western cuisines.
This connection explains why they look and taste similar while maintaining their individual culinary and cultural identities.
Are Calabacita and Zucchini the Same?
This is where things get interesting. While calabacita and zucchini share many similarities, they are not exactly the same. Let’s break it down.
Key Differences Between Calabacita and Zucchini
- Shape and Size:
- Calabacita is generally shorter, rounder, and may have a slightly bulbous shape.
- Zucchini is longer and more uniform, with a cylindrical appearance.
- Skin Color and Texture:
- Calabacita often has lighter green skin or speckles and may feel slightly more textured.
- Zucchini usually has smooth, dark green skin, sometimes with subtle stripes.
- Taste:
- Both have mild flavors, but calabacita is often described as slightly sweeter and nuttier.
- Zucchini has a more neutral taste, making it a versatile base in recipes.
- Regional Use:
- Calabacita is a staple in Latin American dishes, often appearing in traditional stews and sautés.
- Zucchini is more commonly associated with Mediterranean and Western cuisines.
Similarities That Connect Calabacita and Zucchini
Despite their differences, calabacita and zucchini belong to the same family: Cucurbitaceae. They share:
- Culinary Uses: Both are tender and cook quickly, making them ideal for steaming, grilling, and roasting.
- Nutritional Value: Packed with vitamins and minerals, they’re excellent low-calorie options.
- Growing Conditions: Both thrive in warm climates and require similar care when cultivated.
Health Benefits of Calabacita and Zucchini

Both calabacita and zucchini are low-calorie, nutrient-dense vegetables that offer numerous health benefits. Their nutritional profiles make them an excellent addition to a balanced diet. Let’s delve deeper into their health advantages.
Nutritional Comparison
Calabacita and zucchini share many similar nutrients, which are essential for overall health. Below is a detailed breakdown of their nutritional value per 100 grams:
| Nutrient | Calabacita | Zucchini | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~20 kcal | ~17 kcal | Supports weight management due to low calorie count. |
| Water Content | ~94% | ~95% | Helps with hydration and digestion. |
| Vitamin C | 15% of RDI | 17% of RDI | Boosts immunity and promotes healthy skin. |
| Vitamin A | Moderate | High | Supports vision and skin health. |
| Potassium | ~250 mg | ~260 mg | Regulates blood pressure and muscle function. |
| Fiber | ~1.5 g | ~1 g | Improves digestion and promotes gut health. |
| Antioxidants | Moderate | Moderate | Protects against free radical damage. |
Weight Management and Hydration
Both calabacita and zucchini are incredibly low in calories while being high in water content. This combination makes them ideal for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy lifestyle. Their high water content also keeps you hydrated, which is crucial for overall well-being.
Digestive Health
The fiber content in these squashes aids digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fiber also supports a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a key role in overall health and immunity.
Heart Health
Calabacita and zucchini are rich in potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure by balancing sodium levels in the body. This reduces the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, their low-fat content and absence of cholesterol make them heart-healthy choices.
Boosting Immunity
Thanks to their Vitamin C content, both vegetables help strengthen the immune system. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and improving skin health.
Supporting Eye Health
Zucchini, in particular, contains higher levels of Vitamin A, which supports good vision and prevents age-related macular degeneration. Both calabacita and zucchini contain lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that further promote eye health by protecting against UV-induced damage.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
The low glycemic index of calabacita and zucchini makes them excellent for individuals managing diabetes or looking to control blood sugar levels. Their fiber content slows the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes in blood glucose.
Antioxidant Protection
Both squashes are packed with antioxidants like beta-carotene and polyphenols, which help combat inflammation and oxidative stress. These properties are beneficial in reducing the risk of chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease.
Bone Health
Although not widely discussed, calabacita and zucchini contain small amounts of calcium and magnesium, essential minerals that contribute to strong and healthy bones. These nutrients also play a role in muscle function and nerve signaling.
Promoting Healthy Skin
The combination of Vitamin C, antioxidants, and hydration in these squashes promotes radiant and healthy skin. Regular consumption can help reduce signs of aging, such as wrinkles, by boosting collagen production.
Culinary Uses and Recipes: Calabacita vs. Zucchini
Popular Recipes with Calabacita
Calabacita is celebrated in Latin American kitchens. Some popular dishes include:
- Calabacitas con elote: A mixture of sautéed squash, corn, tomatoes, and spices.
- Stuffed Calabacita: Filled with ground meat, rice, or cheese.
- Caldo de Res: A hearty beef soup featuring calabacita chunks.
Delicious Zucchini Recipes
Zucchini, on the other hand, has gained global fame with dishes like:
- Zucchini Noodles (Zoodles): A low-carb pasta alternative.
- Stuffed Zucchini Boats: Filled with quinoa, veggies, or meat.
- Zucchini Bread: A moist, sweet treat perfect for dessert or breakfast.
Substituting Calabacita for Zucchini in Recipes
In most recipes, calabacita can be used as a one-to-one substitute for zucchini. However, because calabacita is slightly sweeter and more tender, it might alter the dish’s flavor slightly—though not in a bad way!
Growing and Harvesting: Calabacita vs. Zucchini
Growing your own calabacita or zucchini can be a rewarding experience. Although they share similar cultivation requirements, there are a few nuances to consider.
Optimal Growing Conditions for Calabacita
Calabacita thrives in warm, sunny climates and requires well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. Key considerations:
- Temperature: Calabacita prefers temperatures between 70°F and 85°F.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Plant Spacing: Allow at least 2 to 3 feet between plants to ensure proper air circulation and growth.
Harvesting calabacita is straightforward. Pick them when they are small and tender, typically around 4 to 6 inches long. Overripe calabacitas may become tough and lose their flavor.
Ideal Environment for Zucchini Growth
Zucchini also thrives in similar conditions. It loves full sun, fertile soil, and consistent watering. Key tips for success:
- Temperature: Zucchini grows best when the soil is warm, ideally above 70°F.
- Fertilizing: Use a balanced fertilizer during the growing season to promote healthy plants.
- Harvest Time: Pick zucchini when they’re about 6 to 8 inches long for the best texture and flavor.
Common Challenges and Pests for Both Plants
Both plants are susceptible to similar pests and diseases:
- Squash Bugs: These pests can damage the leaves and stems. Regular inspection and removal are essential.
- Powdery Mildew: A fungal disease that appears as white spots on leaves. Prevent by ensuring good air circulation and avoiding overhead watering.
- Blossom-End Rot: Often caused by inconsistent watering or a calcium deficiency. Maintain steady moisture levels to prevent this issue.
Calabacita and Zucchini in Global Cuisine
Latin American Dishes Featuring Calabacita
Calabacita is a staple in Latin American cooking, particularly in Mexico. Some standout dishes include:
- Sopa de Calabacita: A creamy soup made with squash, onions, and a touch of cream or cheese.
- Tacos de Calabacita: A vegetarian taco filling made with sautéed calabacita, onions, and spices.
- Enchiladas Verdes con Calabacita: Green enchiladas stuffed with a calabacita-based filling.
Zucchini’s Role in Mediterranean Cooking
Zucchini is a favorite ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine, where its mild flavor complements bold seasonings. Notable dishes include:
- Ratatouille: A French dish featuring zucchini, eggplant, and tomatoes.
- Zucchini Fritters: A Greek-inspired recipe combining grated zucchini, herbs, and feta cheese.
- Stuffed Zucchini with Rice and Lamb: A traditional Middle Eastern dish.
Fusion Cuisine: Bringing Both Together
In today’s globalized kitchens, chefs often experiment with both calabacita and zucchini in fusion dishes. For instance:
- Zucchini and Calabacita Stir-Fry: A blend of Asian and Latin flavors with soy sauce, garlic, and chili.
- Squash Medley Soup: A comforting dish using both types of squash, carrots, and aromatic herbs.
FAQs About Calabacita and Zucchini
Can I use calabacita in place of zucchini in any recipe?
Yes, calabacita works as a direct substitute for zucchini in most recipes. For a delightful option, try this Calabacitas Recipe: A Healthy Mexican Dish.
How can I tell calabacita and zucchini apart in the store?
Calabacita is shorter, rounder, and lighter in color compared to zucchini. Learn more about these distinctions in What is Calabacita Squash? Discover This Incredible Superfood.
Which is healthier: calabacita or zucchini?
Both are highly nutritious, low in calories, and rich in vitamins. They’re nearly identical in health benefits, so you can’t go wrong with either!
Are there other squash varieties similar to calabacita and zucchini?
Yes, other similar varieties include yellow squash, pattypan squash, and certain heirloom squashes.
Do calabacita and zucchini taste the same?
Calabacita is slightly sweeter and nuttier, while zucchini has a more neutral flavor. For pairing ideas, explore What to Serve with Calabacitas.
Conclusion: Similar Yet Unique
Calabacita and zucchini share similarities but remain distinct in flavor, appearance, and cultural significance. Whether you’re cooking traditional Latin American dishes or experimenting with new flavors, both are versatile and nutritious additions to your meals. Dive deeper into this topic with guides like What is Calabacita Squash? Discover This Incredible Superfood and find recipes to highlight their best qualities, such as Calabacitas Con Queso.
By incorporating these insights and recipes, you can fully appreciate the culinary and cultural value of both calabacita and zucchini.